Spring-Boot & Redis Connectivity With Docker/Kubernetes
Introduction
In this article, we will learn on how to establish connectivity with Redis DB using spring-boot & deploying same on Kubernetes cluster.
Pre-Requisites
Editor — IntelliJ Idea/Eclipse
Language — Java 8 or above
Framework — Spring boot
Image Build Tool — Docker
Orchestration — Kubernetes(k8)
Database — Redis
GIT Repo
https://github.com/shethaptech/spring-boot/tree/main/redis-counter-service
Now, lets jump to the design & draw the outline of our implementation.
1. Design
We will design an microservice using spring-boot & jedis client to connect to Redis DB. This application will increment the visitor counter each time visitor visiting our page.
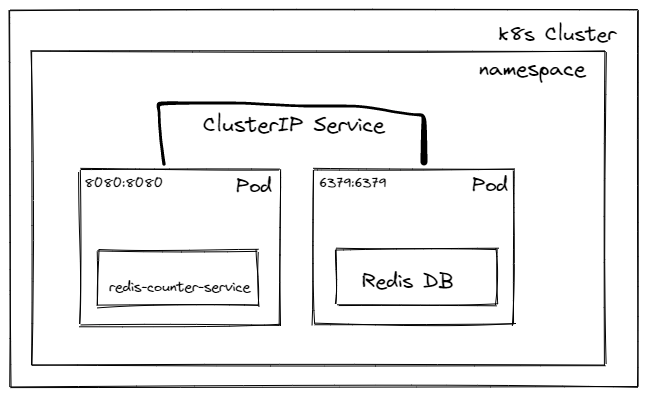
If you will refer to the above high level design,
→ we will have 2 pods running for “redis-counter-service” & Redis db server each.
→ Both pods are connected & will communicate via ClusterIP type k8s service.
→ We have exposed port 8080 for “redis-counter-service” & 6379 for Redis DB server.
→ “redis-counter-service” will connect to Redis DB using k8s service “reddis-db-svc” on port 6379.
2. Redis DB Server
Let’s install Redis DB using its docker image.
2.1 Pull Redis image from the container registry.
docker pull Redis // this will fetch from docker hub by default
2.2 Make Redis container up using image pulled from docker container registry.
docker run -p 6379:6379 — name redis -d redis
2.3 Verify that Redis DB is up.
docker exec -it redis sh
this command will take you to the Redis container’s bash. It implies that Redis container is up & we are able to connect.

Also, you can check logs of the Redis DB container to check if any error during startup or not.

Since we have Redis DB is up & running, Let’s make our service up.
3. Spring-Boot Service Set-up
3.1 Spring data JPA dependency for Redis
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>3.2 Spring boot java client for Redis
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.6.3</version>
</dependency>3.3 Configuration
redis:
# host: 127.0.0.1
host: reddis-db-svc #this should be the k8s service name for Redis
port: 6379Please refer to the git repository for the code base.
4. Docker Image Build — Dockerfile
Please refer to the below configuration to build docker image.
docker build -f <<docker file path>> -t <<tag>>
FROM java
ARG ARTIFACT_NAME=redis-counter-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
ENV ARTIFACT_NAME=${ARTIFACT_NAME}
RUN mkdir /app
COPY target/${ARTIFACT_NAME} /app/
CMD java -jar /app/${ARTIFACT_NAME}5. Container Orchestrations — Kubernetes(k8s)
Here, we will use Kubernetes(k8s) for container orchestrations.
we will create & k8s deployment & service object
Please refer to the git repository for the code base.
→ deploy K8s object using below command.
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
kubectl apply -f service.yaml
→ Verify k8s objects are up & available.
kubectl get svc

kubectl get pod

6. Show Time
Once k8s objects are up & running, hit the below URL. Each time you hit the URL, visit counter will increment
http://127.0.0.1:8080/counter/increment
Key takeaways
So, what we have learnt so far,
→ Spring boot service for visitor’s counter
→ Redis DB server using containerization
→ Docker to build an image
→ Kubernetes deployment & service